Data tests for SQL
You can use data tests to ensure that your business data is generated reliably over time. As a data engineer, data analyst, or business user, you can run data tests so that you don’t have to manually check every dataset every time you run a job or model. The data test checks the validity of the SQL in your project.
A data test is an assertion you make about a dataset in your project. The dataset can be the output from a series of transformations, or the dataset can be a particular data source, seed, or model.
For example, the following test named ref_int_orders_customers checks the validity of the SQL in the HelloWorld_SQL project. In particular, the referential integrity check for orders and customers asserts that every customer_id entry in the orders table is present in the customers table.
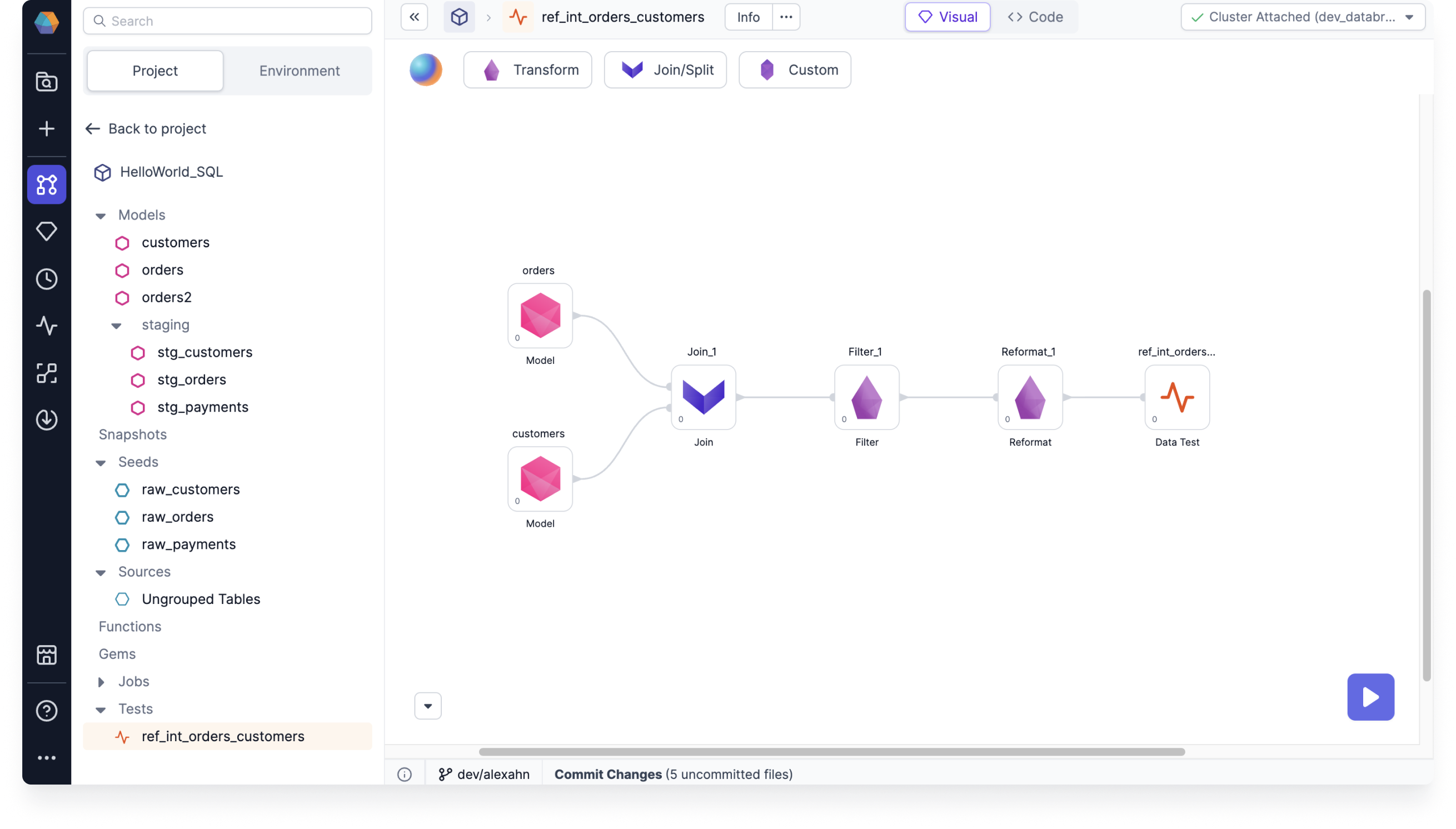
This test starts with several models from the HelloWorld_SQL project, combines their data with a series of transformation steps, and feeds the resulting table into the Data Test gem.
If there are customer_id entries in the orders table that are not present in the customers table, then the ref_int_orders_customers test fails.
You can test any series of transformations with a Data Test gem. The following sections include more details about data tests.
What you'll need to know
Data tests use dbt for the underlying test execution, but you don’t need to know dbt or how to write your own tests. Prophecy simplifies the test definitions that are normally defined in .sql and .yaml files.
You can create data tests in Prophecy using the visual canvas.
Supported database objects
Supported database objects include:
- Models
- Snapshots
- Seeds
- Sources
Data tests can accept input data from any table, no matter if the table is defined by a model, snapshot, seed, or source.
Supported test types
Supported test types include:
- Project tests: Singular use tests that depend on the model that they were created for
- Generic tests: Generic use test that are not tied to a specific model, and can be reused repeatedly
- Model tests
- Column tests
When to use each test type
See a few recommendations in the following table to get an idea of when to use each test type.
| General situations | Project test | Model test | Column test |
|---|---|---|---|
| Test a single Model | |||
| Test multiple Models |
| Specific situations | Project test | Model test | Column test |
|---|---|---|---|
| Test for referential integrity | |||
| Test for late arriving data | |||
| Test for data consistency verification | |||
| Test for model size and aggregations | |||
| Test for column data format and data presence (nulls, empty strings, etc.) |
What's next
To set up a project test, see Use project tests.
If you need to reuse a test that is defined by a parametrized query, see Use model tests.