Secret providers
Secrets help protect sensitive information, such as API keys, passwords, and encryption keys. When you create a fabric, you can add one or more secret providers to manage secrets for that fabric. You can then create and use secrets in your pipelines.
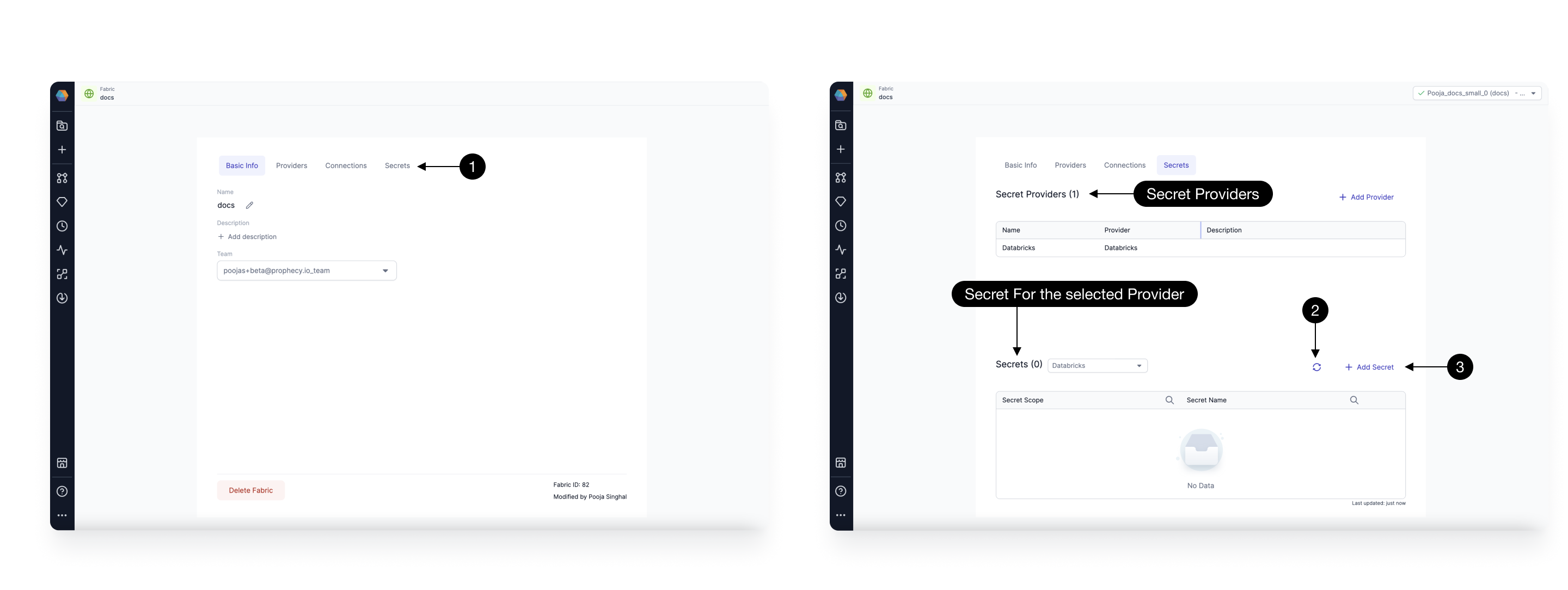
You can configure multiple secret providers per fabric in the Providers tab of the fabric configuration. Providers and secrets can be added, edited, and deleted from Prophecy. We support the following providers.
| Secret Provider | Details | Platform |
|---|---|---|
| Prophecy | Recommended if you use Prophecy Automate | Prophecy |
| Databricks Secrets | Recommended if you are a Databricks user | Databricks |
| HashiCorp Vault | Recommended if your organization privileges HashiCorp Vault | Any Spark |
| Environment Variables | Recommended if your organization privileges environment variables | Any Spark |
If you use a secret provider that isn't listed here, you can still access secrets in your pipeline by calling the provider's API from a Script gem, which runs PySpark code.
Prophecy
Prophecy provides its own secret manager for Prophecy fabrics to securely store both text-based secrets (like passwords) and binary data (such as uploaded certificates). We prioritize the security of your data with advanced encryption techniques designed to protect against unauthorized access. Contact us to learn more about our native secret management.
Databricks
Databricks is the most commonly used secret provider in Prophecy. By default, a Databricks secret provider is added to all Databricks fabrics. You can remove this if required.
If you add new secrets in Databricks, you can refresh secrets in Prophecy to fetch them. You can also add new secrets directly in Prophecy. To refresh or add secrets, you must be attached to a cluster. You can only access secrets that you also can access in Databricks.
If you are using a free trial, you can use Databricks as the secret provider. Your secrets will be automatically cleaned up after the trial expires. While Prophecy assigns a separate scope to each Prophecy-managed fabric, it is not recommended to use your production data tools for trials.
HashiCorp Vault
Prophecy supports HashiCorp Vault as a secret provider. When you set up HashiCorp Vault, you'll see a few additional configuration fields.
- Namespace: An optional field to specify the namespace within a multi-tenant Vault.
- Address: Auto-filled from Spark cluster. You must first set up a
VAULT_ADDRenvironment variable in the Spark cluster. - Token: Auto-filled from Spark cluster. You must first set up a
VAULT_TOKENenvironment variable in the Spark cluster.
If you add new secrets to your vault, you can refresh secrets in Prophecy to fetch them. You can also add new secrets directly in Prophecy. To refresh or add secrets, you must be attached to a cluster. You can only access secrets that you also have access to in your Spark cluster.
Environment Variables
If you prefer a simple way to manage secrets, you can use environment variables available in your Spark cluster. To do so:
- Add a new secret provider and choose Environment.
- Add a new secret. Prophecy will automatically map this secret to an environment variable in your Spark cluster.
- Verify that the new environment variable exists in your Spark cluster with the correct value.
This method does not support refreshing or fetching secrets.