Scheduling
Prophecy supports the following ways to automate pipeline execution.
- Built-in scheduler: Use Prophecy Automate to orchestrate pipelines directly in the UI.
- Pipeline gem: Configure the Pipeline gem to start pipeline runs from a gem in the canvas.
- API-based automation: Call the Trigger Pipeline API to start pipelines from external systems.
This page describes how to use the built-in scheduler in SQL projects.
Overview
In Prophecy, a schedule automates the execution of a single pipeline in a project. Scheduled pipelines run in fabrics (execution environments) that are defined during project publication. Each schedule defines:
- When the pipeline should run. Prophecy supports time-based or file-based triggers.
- Optional email alerts to report the outcome of the pipeline run.
To schedule multiple pipelines, create a separate schedule for each one. You can enable or disable schedules individually, but enabling a schedule doesn’t activate it. An enabled schedule becomes active only when the parent project is published. Similarly, disabling a schedule also requires republishing the project, since schedule status is part of the deployment configuration.
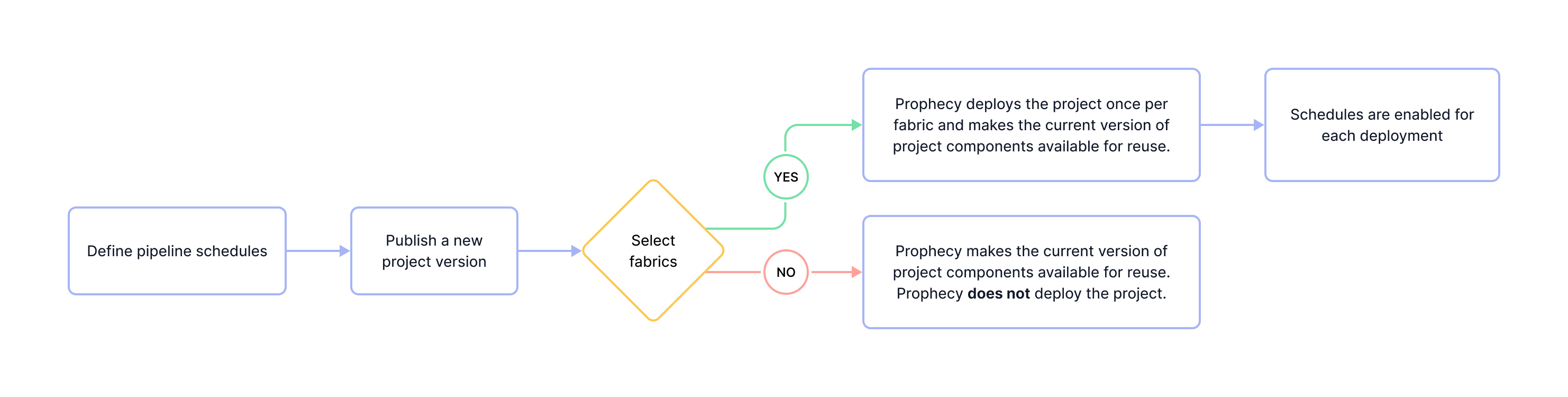
Schedule activation
Enabling a schedule in your project doesn't immediately activate it. For a schedule to take effect, you must first publish the project. This is because publishing defines how and where scheduled pipelines are deployed and executed.
When you publish a project, you do two key things:
-
Select one or more fabrics. These are the environments where scheduled pipelines will run. A separate deployment is created for each fabric — publishing to one fabric does not affect other deployments.
If you do not select any fabrics during project publication, no deployments will be created. As a result, no scheduled executions will occur, even if a schedule has been configured.
-
Specify the project version. This version will be deployed to the fabric. You can either create a new version or deploy a previously published version.
Monitor scheduled pipelines
You and your team members might have many scheduled pipelines in your Prophecy environment. The Observability interface in Prophecy includes the following information:
- List of deployed projects
- List of pipeline schedules per fabric
- History of pipeline runs and run status
You'll only see information about projects owned by your teams.
Authentication lifespan
Scheduled pipelines run without human intervention, which makes them vulnerable to failures caused by expired or invalid credentials. If Prophecy cannot authenticate a connection used by the pipeline due to an error such as an expired token or deleted user, the pipeline run will fail.
This risk increases in complex environments where:
- Pipelines depend on multiple external data sources.
- The same schedule is deployed across multiple fabrics.
- Fabrics store different credentials for the same connection.
To ensure reliable scheduled runs, only deploy to fabrics that use connection credentials that won’t expire unexpectedly. For Databricks connections, consider using a service principal for authentication. Service principals are designed for authorizing access to Databricks resources when running unattended processes.
What's next
To learn more about using the Prophecy-native scheduler, explore the following pages.
Set up schedule
Automate a pipeline with the Prophecy scheduler
Schedule trigger types
Learn about different trigger types for schedules
Pipeline gem
Start pipeline runs from a gem in the canvas
Email alerts
Report the outcome of a scheduled pipeline run