SpatialMatch gem
Use the SpatialMatch gem to find relationships between geometries from two different datasets. Common use cases include:
- Finding which stores are located within specific delivery zones
- Identifying roads that intersect with flood zones
- Matching customer locations to their nearest service areas
The gem uses spatial joins to compare geometries and returns only the pairs that have the spatial relationship you specify, such as shapes overlapping or shapes touching. It works with points, lines, and polygons in Well-Known Text (WKT) format.
The SpatialMatch gem has a corresponding interactive gem example. See Interactive gem examples to learn how to run sample pipelines for this and other gems.
Use the following gems to create correctly formatted geometries in a dataset:
- CreatePoint gem for points
- PolyBuild gem for lines and polygons
Input and Output
The SpatialMatch gem accepts the following inputs and output.
| Port | Description |
|---|---|
| in0 | Dataset containing geometries (points, lines, or polygons) in WKT format. This is the "left" dataset in the spatial join operation. |
| in1 | Dataset containing geometries (points, lines, or polygons) in WKT format. This is the "right" dataset in the spatial join operation. |
| out | Output dataset containing matched pairs of geometries along with all additional columns from both input datasets. Each row represents a source geometry and target geometry that satisfy the selected spatial relationship. Unmatched geometries are excluded from the output. The output includes the following columns:
|
You can use the same source for both in0 and in1 if you want to match geometries from the same dataset (self-join).
Parameters
Configure the SpatialMatch gem using the following parameters.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Source Column | Select the column from in0 that contains one set of geometric data. |
| Target Column | Select the column from in1 that contains another set of geometric data. |
| Select Match Type | Choose the spatial relationship that determines when a source geometry matches a target geometry. Learn more in Match types. |
Match types
Review the following to understand the criteria to satisfy different match types. The SpatialMatch gem returns a row for each match condition that is met.
| Match type | Description |
|---|---|
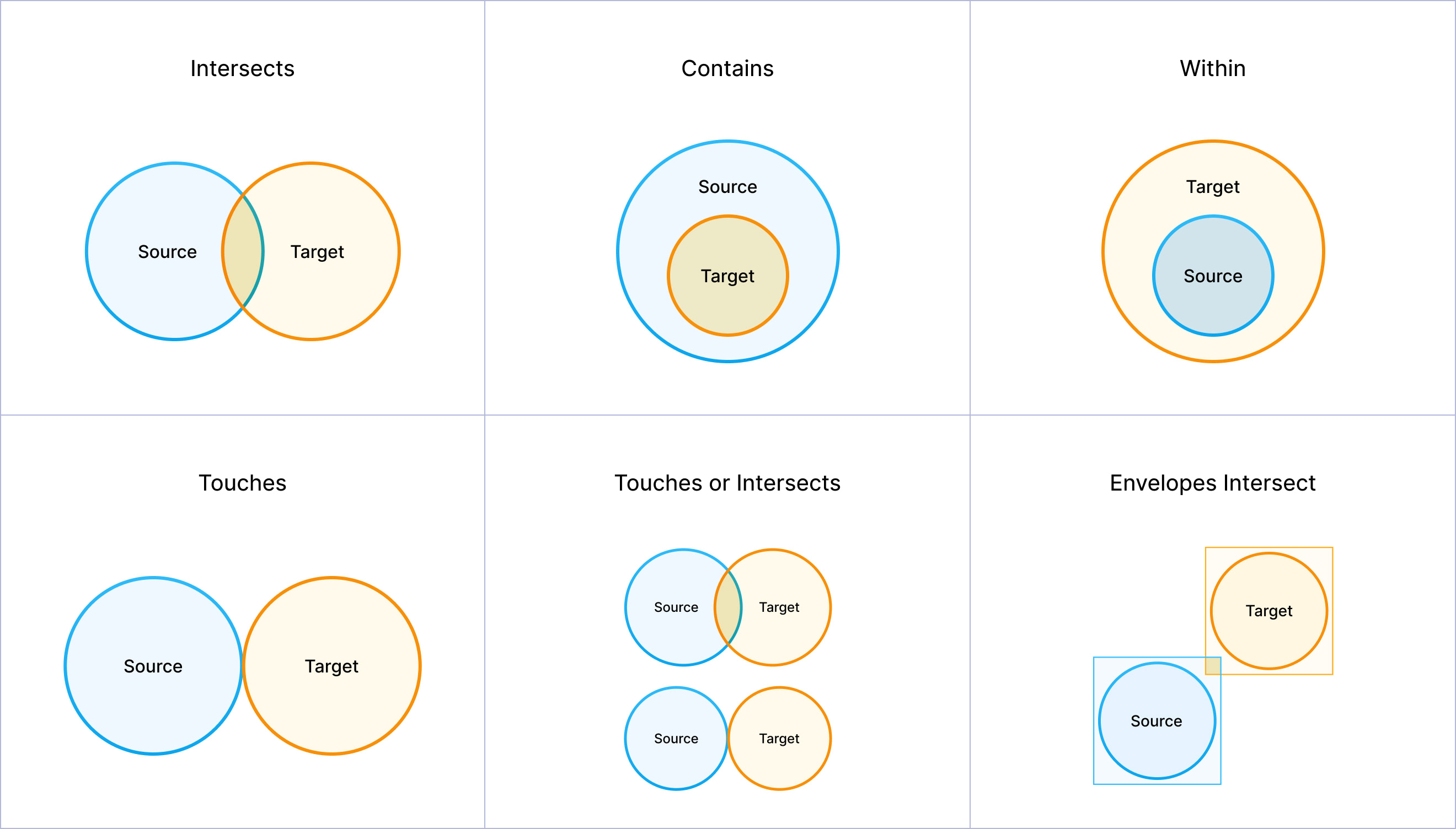
| Source Intersects Target | Condition is met if the source and target geometries share any portion of space. This is the most general spatial relationship. Any overlap, touching, or containment satisfies intersection. |
| Source Contains Target | Condition is met if the source geometry completely contains the target geometry. The target geometry must be entirely within the source geometry's interior and boundary. |
| Source Within Target | Condition is met if the source geometry is completely contained within the target geometry. This is the inverse of the Contains relationship. |
| Source Touches Target | Condition is met if the source and target geometries have at least one point in common, but their interiors do not intersect. |
| Source Touches or Intersects Target | Condition is met if the source and target geometries either touch (share boundary points) or intersect (share any portion of space). This combines the touch and intersect relationships. |
| Source Envelope Overlaps Target Envelope | Condition is met if the minimum bounding rectangles (envelopes) of the source and target geometries overlap. This is a less precise check than a standard intersection. |
Match types diagram
The following diagram includes visualizations for each match type.
Example: Find stores within delivery zones
Assume you have two datasets:
-
store_locationscontains store locations as points.store_id store_name store_location store_type 1 Downtown Electronics POINT(-74.0059 40.7128) electronics 2 Midtown Cafe POINT(-73.9857 40.7489) restaurant 3 Brooklyn Bookstore POINT(-73.9442 40.6782) bookstore 4 Queens Pharmacy POINT(-73.7949 40.7282) pharmacy 5 Upper East Side Boutique POINT(-73.9626 40.7831) clothing -
delivery_zonescontains delivery zones as polygons.zone_id zone_name zone_polygon delivery_fee MANHATTAN_SOUTH Lower Manhattan POLYGON((-74.0200 40.7000, -74.0200 40.7300, -73.9800 40.7300, -73.9800 40.7000, -74.0200 40.7000)) 5.99 MANHATTAN_NORTH Upper Manhattan POLYGON((-73.9800 40.7700, -73.9800 40.8000, -73.9400 40.8000, -73.9400 40.7700, -73.9800 40.7700)) 7.99 BROOKLYN_WEST Western Brooklyn POLYGON((-74.0000 40.6500, -74.0000 40.7000, -73.9200 40.7000, -73.9200 40.6500, -74.0000 40.6500)) 6.99 QUEENS_CENTRAL Central Queens POLYGON((-73.8500 40.7000, -73.8500 40.7500, -73.7500 40.7500, -73.7500 40.7000, -73.8500 40.7000)) 8.99
To find which delivery zones correspond to each store:
- Add a SpatialMatch gem to your pipeline canvas.
- Attach
store_locationsto the in0 port of the gem. - Attach
delivery_zonesto the in1 port of the gem. - Open the gem configuration interface.
- For the Source field, select the
store_locationcolumn from thestore_locationstable. - For the Target field, select the
zone_polygoncolumn from thedelivery_zonestable. - Under Select Match Type, select Source Within Target.
- Save and run the gem.
Result
The SpatialMatch gem will return only the pairs of geometries that satisfy the selected match type. As a result:
- Downtown Electronics matches the
MANHATTAN_SOUTHzone. - Queens Pharmacy matches the
QUEENS_CENTRALzone. - Upper East Side Boutique matches the
MANHATTAN_NORTHzone. - Midtown Cafe does not match any zone. This means that it is not in any delivery zone.