Gems
Gems are functional units in a pipeline that perform tasks such as reading, transforming, writing, or handling other data operations. When you build pipelines in a SQL project, some gems will be powered by Prophecy Automate, and some gems will be powered by SQL dbt.
Prophecy's AI agent can help you build, refine, and explain gems throughout your pipeline. To learn more, see AI & Agents.
Categories
| Category | Description |
|---|---|
| Source/Target | Read and write data from various data providers. |
| Transform | Modify, enrich, or reshape data during processing. |
| Prepare | Clean, structure, and optimize data for analysis. |
| Join | Merge, split, or link datasets. |
| Parse | Parse individual columns that contain formats like XML and JSON. |
| Report | Share results through channels such as email or Tableau. |
| Custom | Enhance and extend Prophecy’s functionality. |
| Spatial | Work with geographic data, such as locations, distances, and areas. |
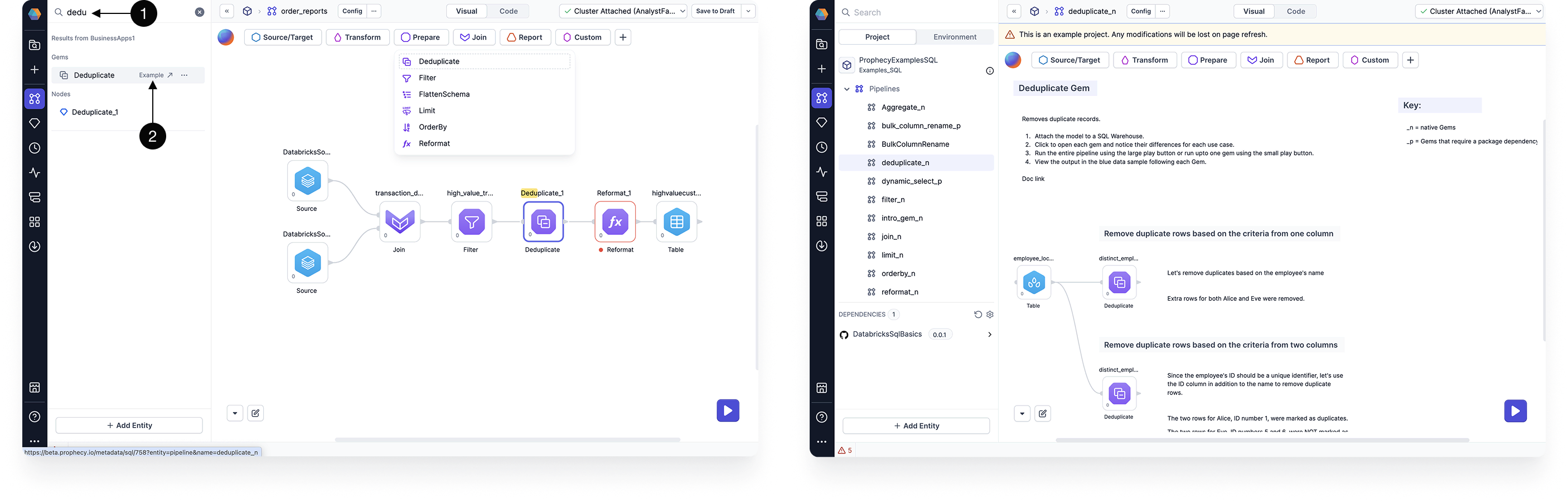
Interactive gem examples
To test a gem hands-on, you can try the interactive example of the gem. If you search for a gem in the project sidebar, you can open the associated example and run the preconfigured pipeline!
Expressions
Many gems include expression components where you can implement custom or complex logic. You can either build expressions visually, or use SQL syntax to write expression in code. Prophecy will automatically convert visual expressions to code expressions, and vice versa.
The SQL dialect for expressions depends on the SQL warehouse connection of the fabric. This is because the project code must be compatible with the execution environment it runs on. Because of this, expressions may look different across projects that run on Databricks versus Snowflake, for example.
Gem instance
When you click on a gem from the gem drawer, an instance of that gem gets added to your pipeline canvas. Use the image and the table below to understand the UI of a gem.
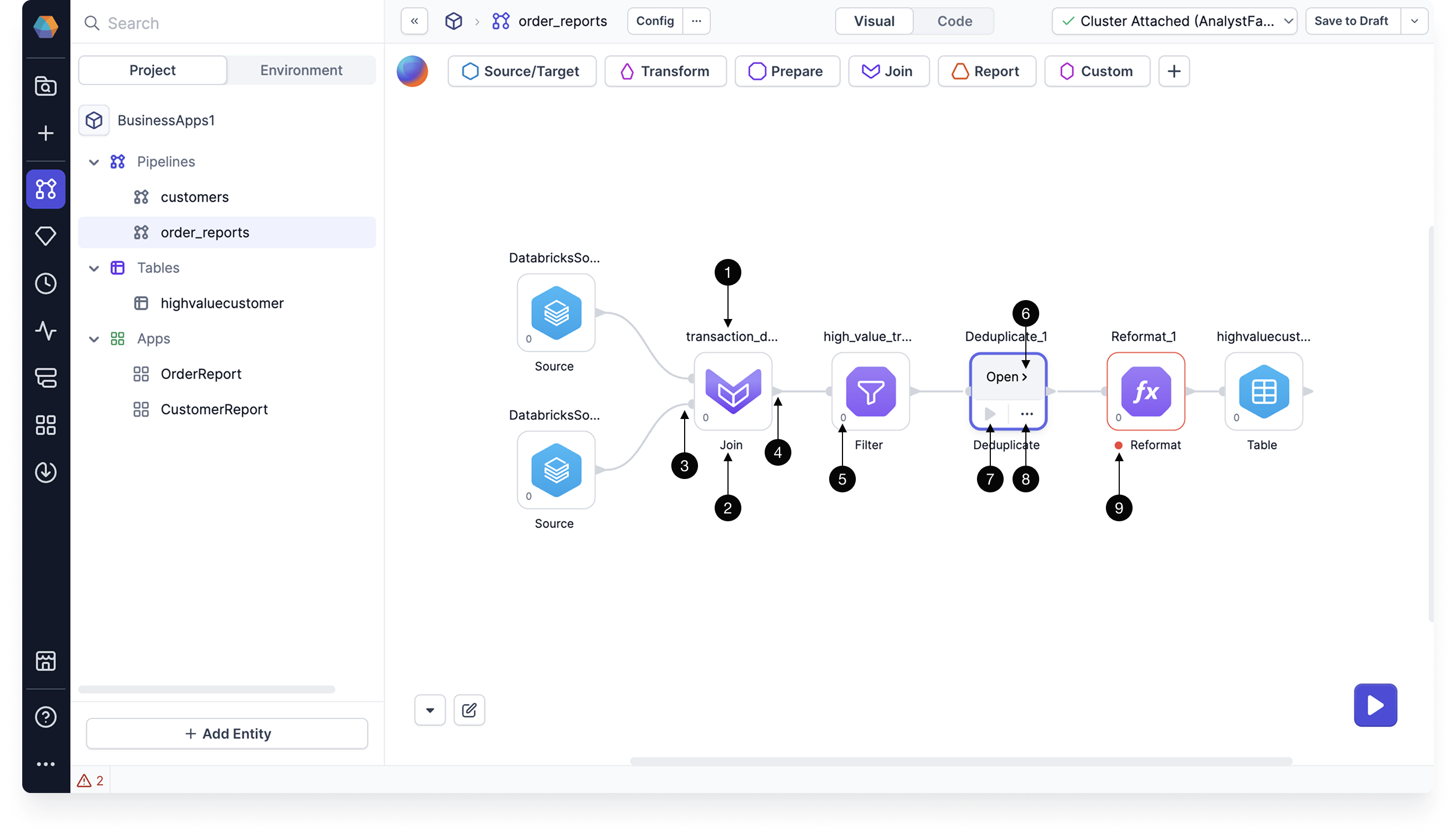
| Callout | UI element | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Gem label | The name of this particular gem instance. It must be unique within a given pipeline. |
| 2 | Gem type name | The type of gem. |
| 3 | Input ports | One or more ports that accept connections from upstream gems. |
| 4 | Output ports | One or more ports that connect to downstream gems. |
| 5 | Gem phase | The phase for this gem instance, which defines the order in which gem instances are executed. |
| 6 | Open | The button that lets you open the gem configuration. |
| 7 | Run button | A button that runs the pipeline up to and including the gem. |
| 8 | Action menu | A menu that includes options to change the phase of the gem, add run conditions, delete the gem, and more. |
| 9 | Warning | Indicator that the gem contains errors to be fixed. |
If you select one or more gems, you can copy and paste them within the same pipeline or across pipelines. However, you cannot paste across projects that use different languages (for example, from SQL to Scala).
Gem configuration
When you open a gem, you can configure how the gem will work. Explore our individual gem documentation to understand each gem's parameters.
Gem ports
Each gem handles ports differently. Some require specific input and output ports. Others allow only one port or none at all. Refer to the documentation for each gem to understand its port requirements.
To add a port:
- Open the gem to access its configuration.
- On the left, choose the Input or Output tab under Ports.
- Click the
+button next to Ports. If the+button doesn’t appear, the gem does not support adding more ports.
To remove ports from a gem:
- Open the gem to access its configuration.
- On the left, choose the Input or Output tab under Ports.
- Click the pencil icon to enter Edit mode.
- Hover over the port you want to remove and click the trash icon.
- Click Done to save your changes and exit Edit mode.
To hide ports from the gem configuration, you can collapse the ports panel using the collapse icon next to Ports.
Visual and code view
Some gems can be configured in the visual view or the code view. Use the visual expression builder to populate fields in the visual view. Prophecy will automatically convert visual expressions into SQL expressions. You can edit these SQL statements or write your own in the code view.
Action menu
The action menu gives you more granular control over individual gems. When you expand the action menu, you see the following options:
| Action | Description |
|---|---|
| Explain | Copilot provides an explanation of what the gem does in the pipeline. |
| Fix | Copilot resolves an error in the gem configuration. |
| Label | Copilot renames the gem. |
| Add Comment | Manually write a comment that appears as a tooltip above the gem. |
| Change Phase | Change the phase of the gem. |
| Delete | Remove the gem from the pipeline. |
Gem phase
In a data pipeline, the phase of a gem determines the sequence in which it runs. Here’s how it works:
- Gems are assigned a numerical phase (e.g.,
0,1,-1), where lower values run first. For example, a gem with phase0will execute before a gem with phase1. - When a gem runs, all its upstream gems must also run. This means that if a downstream gem has phase
0and an upstream gem has phase1, the upstream gem will be grouped into phase0to ensure proper execution. - Because of this dependency, the phase assigned to the last gem in a branch determines the phase of the entire branch. This means that when configuring gem phases, you only need to focus on the leaf nodes—the final gems in each branch of the pipeline.
Normally, pipeline branches run in parallel. Using gem phases, you can develop your pipeline to run in different stages. This can be useful when one part of the pipeline depends on the results of another, allowing you to control the execution order and ensure that data flows correctly from one stage to the next.