Fabrics
Before you can run a pipeline, you need to define an execution environment where the pipelines will run. In Prophecy, you do this by creating fabrics.
A fabric specifies everything required for execution, most importantly the connection to compute, whether it be a Spark cluster or SQL warehouse. When you open a project and attach a fabric, you'll have access to all of the fabric's resources to run your pipelines.
Fabrics are automatically provisioned for users on the Professional Edition.
Fabric types
Different fabrics are designed to support specific project types. Use the table below to identify which fabric best aligns with your project's execution requirements.
| Fabric type | Description | Usage |
|---|---|---|
| Prophecy | Compute with Prophecy Automate and a SQL warehouse | Run pipelines in SQL projects. |
| Spark(Enterprise only) | Compute with a Spark engine | Run pipelines in PySpark/Scala projects and Databricks jobs. |
| SQL(Enterprise only) | Compute with a SQL warehouse | Run models in SQL projects. You cannot run pipelines. |
Fabrics are configured by team admins. To learn how to create each type of fabric listed here, see Fabric setup in the Administration documentation.
Separate environments and access
Fabrics provide a structured way to separate working environments with team-based access. At minimum, you might have a development and production environment, but you may also have fabrics for QA, Staging, etc.
- Development fabric: Environment used for testing and experimentation, where pipelines can be iterated on without impacting live data or processes.
- Production fabric: Environment hosts stable, validated pipelines that process live data for business operations.
When you create a fabric, you assign it to a team. Only users in that team can access the fabric. To control access in your production environment, create a team with only those users who can execute and deploy pipelines in production.
To learn more about the relationship between fabrics, projects, and teams, visit Team-based access.
Fabric usage
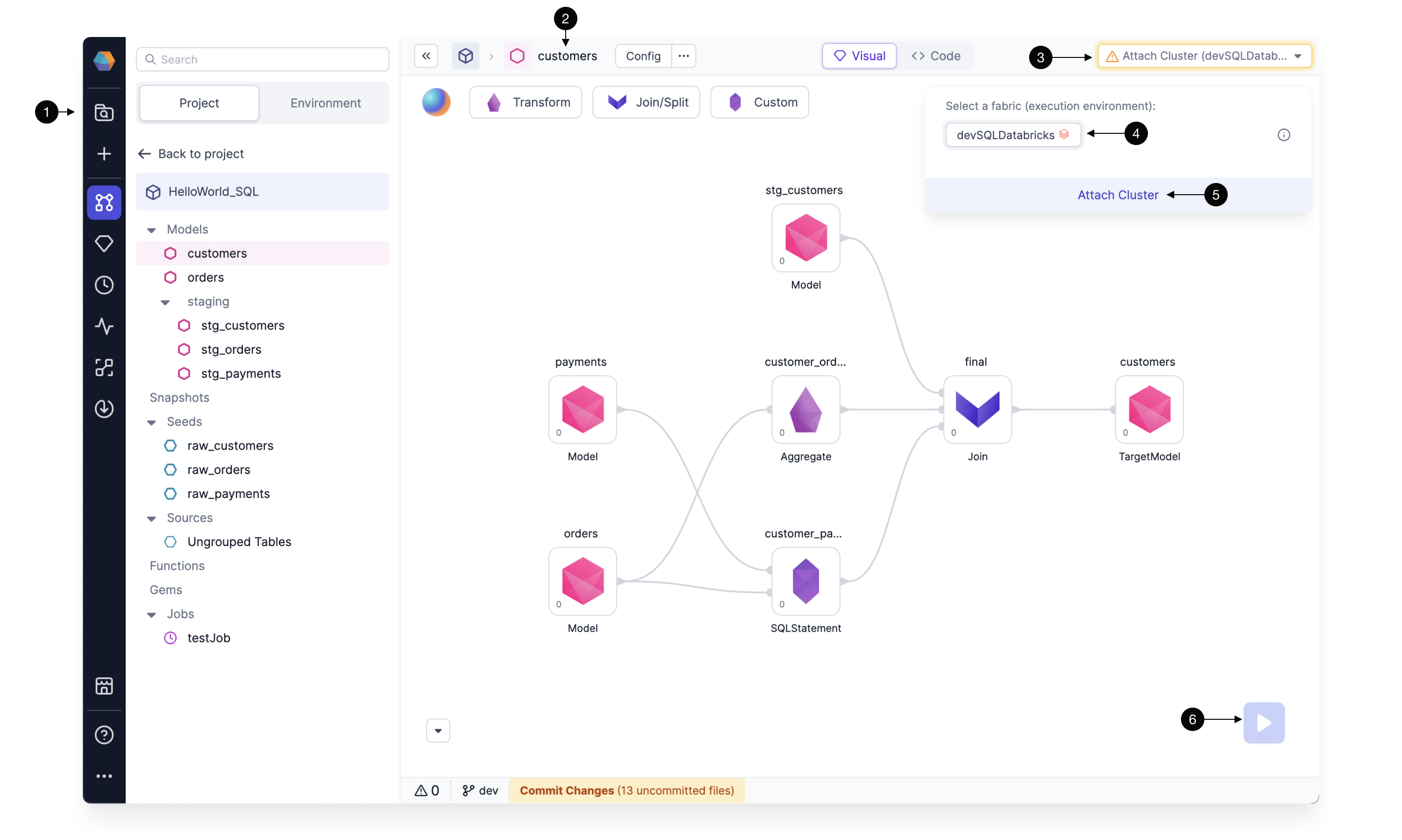
To execute your pipelines, you must attach a fabric to your project, as fabrics define the project's execution environment. You can switch between different fabrics within a project based on factors such as whether you want to use a development or production execution environment. All fabrics created for your teams will be available for you to view and use.
To attach a fabric to a project:
- Open the project editor.
- Expand the Attach Cluster menu in the top right.
- Select a fabric.
- Attach to a cluster or create a new cluster.
- Run your pipeline or model. This executes the data transformation on the environment defined in the fabric.
Fabric metadata
In Prophecy, metadata refers to structured information about all the assets in your workspace. In other words, metadata in Prophecy is the control plane information. You can see this information in the Metadata interface in Prophecy.
If you want to see all of the fabrics owned by your teams, navigate to the Fabrics tab of the Metadata page. Then, click into each fabric to access the fabric settings. These will resemble the settings that appear during fabric creation.
Only team admins can update the fabric settings. Other users in the team may only view the fabric settings as readers.