Avro
The Avro file type:
- Is a row-based, open-source data serialization system.
- Supports schema evolution, which allows schemas to evolve over time without breaking compatibility.
- Stores the data in a binary format, which makes the data compact and efficient.
- Usually appears in big data environments, data streaming applications, and scenarios where data serialization and storage are important.
Parameters
| Parameter | Tab | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Location | File path to read from or write to the Avro file. |
| Schema | Properties | Schema to apply on the loaded data. In the Source gem, you can define or edit the schema visually or in JSON code. In the Target gem, you can view the schema visually or as JSON code. |
Source
The Source gem reads data from Avro files and allows you to optionally specify the following additional properties.
Source properties
| Property name | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
| Description | Description of your dataset. | None |
| Use user-defined schema | Whether to use the schema you define. | false |
| Ignore files without .avro extension while reading | DEPRECATED. Whether to load files without the .avro extension. This parameter will be removed in a future release. To filter file names, use the Path Glob Filter property. | true |
| Recursive File Lookup | Whether to recursively load files and disable partition inferring. If the data source explicitly specifies the partitionSpec when therecursiveFileLookup is true, the Source gem throws an exception. | false |
| Path Global Filter | Glob pattern to only include files with paths matching the pattern. The syntax follows GlobFilter and does not change the behavior of partition discovery. | None |
| Modified Before | Timestamp to only include files with modification times occurring before the time you specify. The timestamp must be in the following format: YYYY-MM-DDTHH:mm:ss (e.g. 2020-06-01T13:00:00) | None |
| Modified After | Timestamp to only include files with modification times occurring after the time you specify. The timestamp must be in the following format: YYYY-MM-DDTHH:mm:ss (e.g. 2020-06-01T13:00:00) | None |
| Avro Schema | Additional schema a user provides in JSON format. To learn more, see Schema evolution. | None |
Schema evolution
When reading an Avro file, you can set the Avro Schema parameter to a newer evolved schema, which is compatible but different from the schema written to storage. The resulting DataFrame follows the newer evolved schema.
For example, if you set an evolved schema to contain one additional column with a default value, the resulting DataFrame contains the new column too.
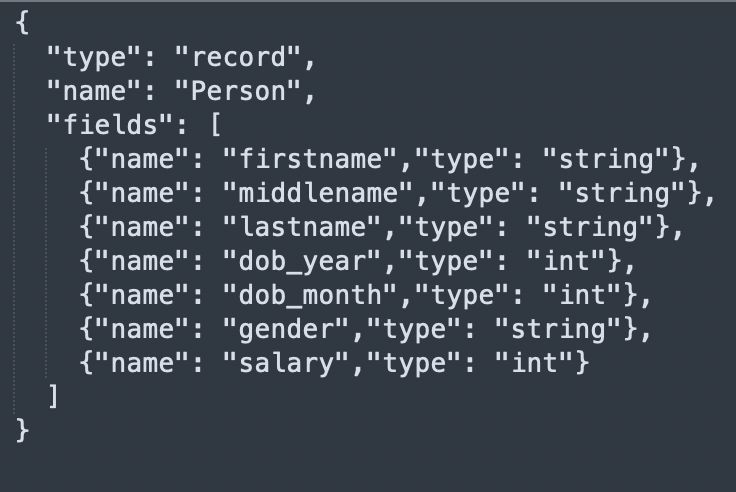
Example
Schema used in example above
Compiled code
To see the compiled code of your project, switch to the Code view in the project header.
- Python
- Scala
def read_avro(spark: SparkSession) -> DataFrame:
return spark.read\
.format("avro")\
.option("ignoreExtension", True)\
.option(
"avroSchema",
"{\"type\":\"record\",\"name\":\"Person\",\"fields\":[{\"name\":\"firstname\",\"type\":\"string\"},{\"name\":\"middlename\",\"type\":\"string\"},{\"name\":\"lastname\",\"type\":\"string\"},{\"name\":\"dob_year\",\"type\":\"int\"},{\"name\":\"dob_month\",\"type\":\"int\"},{\"name\":\"gender\",\"type\":\"string\"},{\"name\":\"salary\",\"type\":\"int\"}]}"
)\
.load("dbfs:/FileStore/Users/abhinav/avro/test.avro")
object read_avro {
def apply(spark: SparkSession): DataFrame =
spark.read
.format("avro")
.option("ignoreExtension", true)
.option(
"avroSchema",
"{\"type\":\"record\",\"name\":\"Person\",\"fields\":[{\"name\":\"firstname\",\"type\":\"string\"},{\"name\":\"middlename\",\"type\":\"string\"},{\"name\":\"lastname\",\"type\":\"string\"},{\"name\":\"dob_year\",\"type\":\"int\"},{\"name\":\"dob_month\",\"type\":\"int\"},{\"name\":\"gender\",\"type\":\"string\"},{\"name\":\"salary\",\"type\":\"int\"}]}"
)
.load("dbfs:/FileStore/Users/abhinav/avro/test.avro")
}
Target
The Target gem writes data to Avro files and allows you to optionally specify the following additional properties.
Target properties
| Property name | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
| Description | Description of your dataset. | None |
| Avro Schema | Additional schema a user provides in JSON format. You can set this parameter if the expected output Avro schema doesn't match the schema Spark converts. For example, the expected schema of a column is an enum type, instead of a string type in the default converted schema. | None |
| Write Mode | How to handle existing data. For a list of the possible values, see Supported write modes. | error |
| Compression | Compression codec when writing to the Avro file. The Avro file supports the following codecs: uncompressed, snappy, deflate, bzip2, and xz. This defaults to the value of the spark.sql.avro.compression.codec parameter. | snappy |
| Partition Columns | List of columns to partition the Avro files by. | None |
| Record Name | Top level record name in the result. | topLevelRecord |
| Record Namespace | Record namespace in the result. | "" (empty string) |
Supported write modes
| Write mode | Description |
|---|---|
| error | If the data already exists, throw an exception. |
| overwrite | If the data already exists, overwrite the data with the contents of the DataFrame. |
| append | If the data already exists, append the contents of the DataFrame. |
| ignore | If the data already exists, do nothing with the contents of the DataFrame. This is similar to the CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS clause in SQL. |
Example
Compiled code
To see the compiled code of your project, switch to the Code view in the project header.
- Python
- Scala
def write_avro(spark: SparkSession, in0: DataFrame):
in0.write\
.format("avro")\
.mode("overwrite")\
.partitionBy("dob_year","dob_month")\
.save("dbfs:/data/test_output.avro")
object write_avro {
def apply(spark: SparkSession, in: DataFrame): Unit =
in.write
.format("avro")
.mode("overwrite")
.partitionBy("dob_year","dob_month")
.save("dbfs:/data/test_output.avro")
}