Kafka
The Kafka file type is used in Apache Kafka. Read and write Kafka files using a Source or Target gem.
Source
The Source gem reads data from Kafka stream in batch mode and allows you to optionally specify the following additional properties. This means that Kafka only reads data incrementally from the last offset stored in the specified Metadata table. If the Metadata table is not present, then Kafka reads data from the earliest offset.
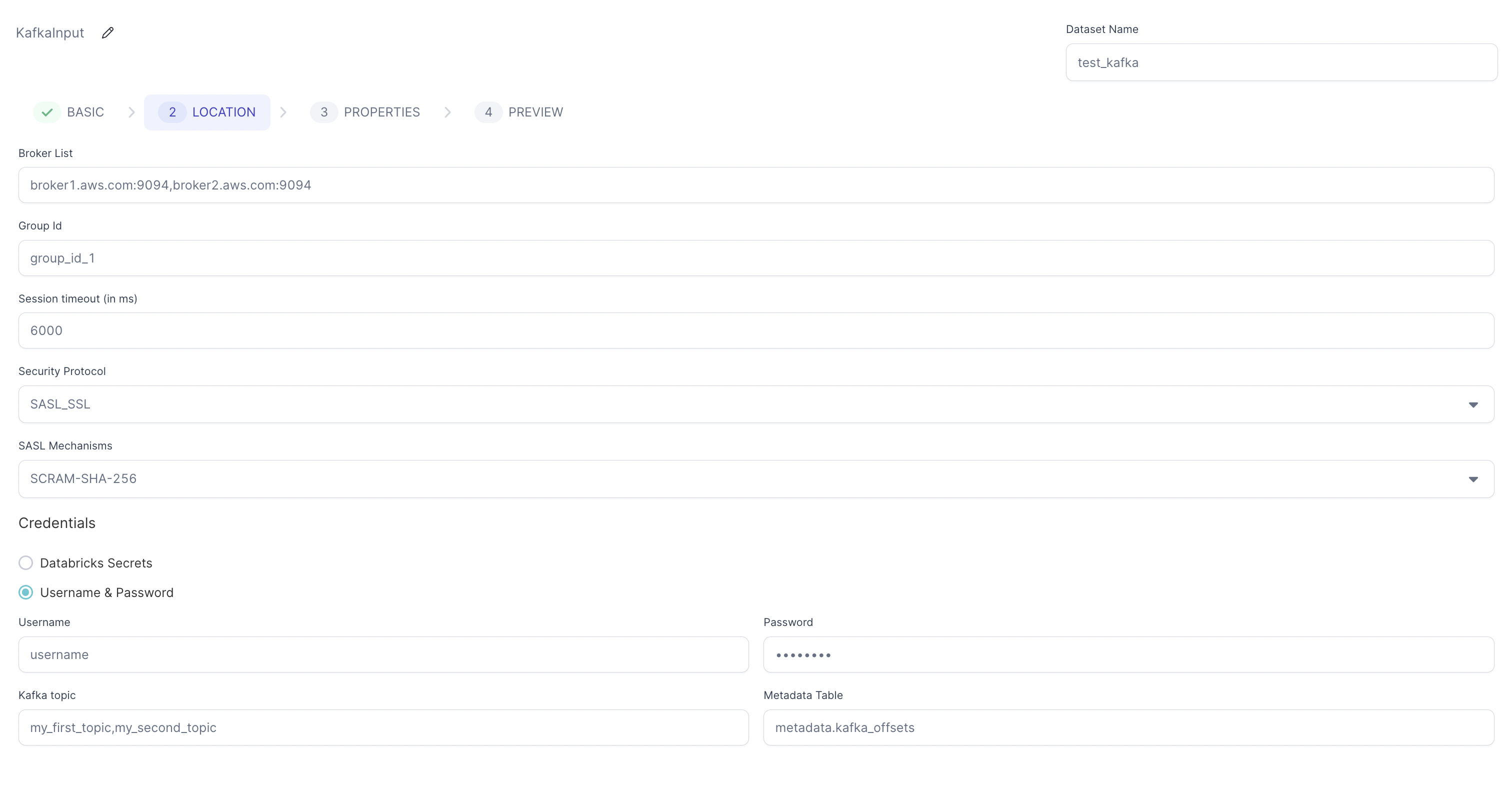
Source location
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Bootstrap Server/Broker List | Comma separated list of Kafka brokers. |
| Group Id (Optional) | Kafka consumer group ID. Used to identify the consumer group for offset management. |
| Session timeout (in ms) | Session timeout for Kafka consumer. Default: 6000 |
| Security Protocol | Security protocol for Kafka. Default value is NO_AUTH. |
| SASL Mechanisms | SASL Mechanism for authentication. Default value is NO_AUTH. |
| Credentials | How to provide your credentials. You can select: Databricks Secrets, Username & Password, Environment variables, or None |
| Kafka topic | Comma separated list of Kafka topics. |
| Store offsets read per partition in Delta table | Whether to store offsets read per partition in Delta table. Default: false |
| Metadata Table | Delta table to store offsets for each topic and partition. |
| Use SSL Trust Store | Enable SSL trust store configuration. |
| Trust Store Location | Path to the SSL trust store file. Required when SSL Trust Store is enabled. |
| Trust Store Password | Password for the SSL trust store file. Required when SSL Trust Store is enabled. |
Source properties
| Property name | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
| Kerberos service name for Kafka SASL | Name of your Kerberos service to use in Kafka. | None |
Example
Compiled code
To see the compiled code of your project, switch to the Code view in the project header.
- Python
def KafkaSource(spark: SparkSession) -> DataFrame:
from delta.tables import DeltaTable
import json
from pyspark.dbutils import DBUtils
if spark.catalog._jcatalog.tableExists(f"metadata.kafka_offsets"):
offset_dict = {}
for row in DeltaTable.forName(spark, f"metadata.kafka_offsets").toDF().collect():
if row["topic"] in offset_dict.keys():
offset_dict[row["topic"]].update({row["partition"] : row["max_offset"] + 1})
else:
offset_dict[row["topic"]] = {row["partition"] : row["max_offset"] + 1}
return (spark.read\
.format("kafka")\
.options(
**{
"kafka.security.protocol": "NO_AUTH",
"kafka.sasl.mechanism": "NO_AUTH",
"kafka.bootstrap.servers": "broker1.aws.com:9094,broker2.aws.com:9094",
"kafka.session.timeout.ms": "6000",
"group.id": "group_id_1",
"subscribe": "my_first_topic,my_second_topic",
"startingOffsets": json.dumps(offset_dict),
"kafka.ssl.truststore.location": "dbfs:/Volumes/tmp/kafka.client.truststore.jks",
"kafka.ssl.truststore.password": "password",
}
)\
.load()\
.withColumn("value", col("value").cast("string"))\
.withColumn("key", col("key").cast("string")))
else:
return (spark.read\
.format("kafka")\
.options(
**{
"kafka.security.protocol": "NO_AUTH",
"kafka.sasl.mechanism": "NO_AUTH",
"kafka.bootstrap.servers": "broker1.aws.com:9094,broker2.aws.com:9094",
"kafka.session.timeout.ms": "6000",
"group.id": "group_id_1",
"subscribe": "my_first_topic,my_second_topic",
"kafka.ssl.truststore.location": "dbfs:/Volumes/tmp/kafka.client.truststore.jks",
"kafka.ssl.truststore.password": "password",
}
)\
.load()\
.withColumn("value", col("value").cast("string"))\
.withColumn("key", col("key").cast("string")))
Target
The Target gem writes data to each row from the Dataframe to a Kafka topic as JSON messages and allows you to optionally specify the following additional properties.
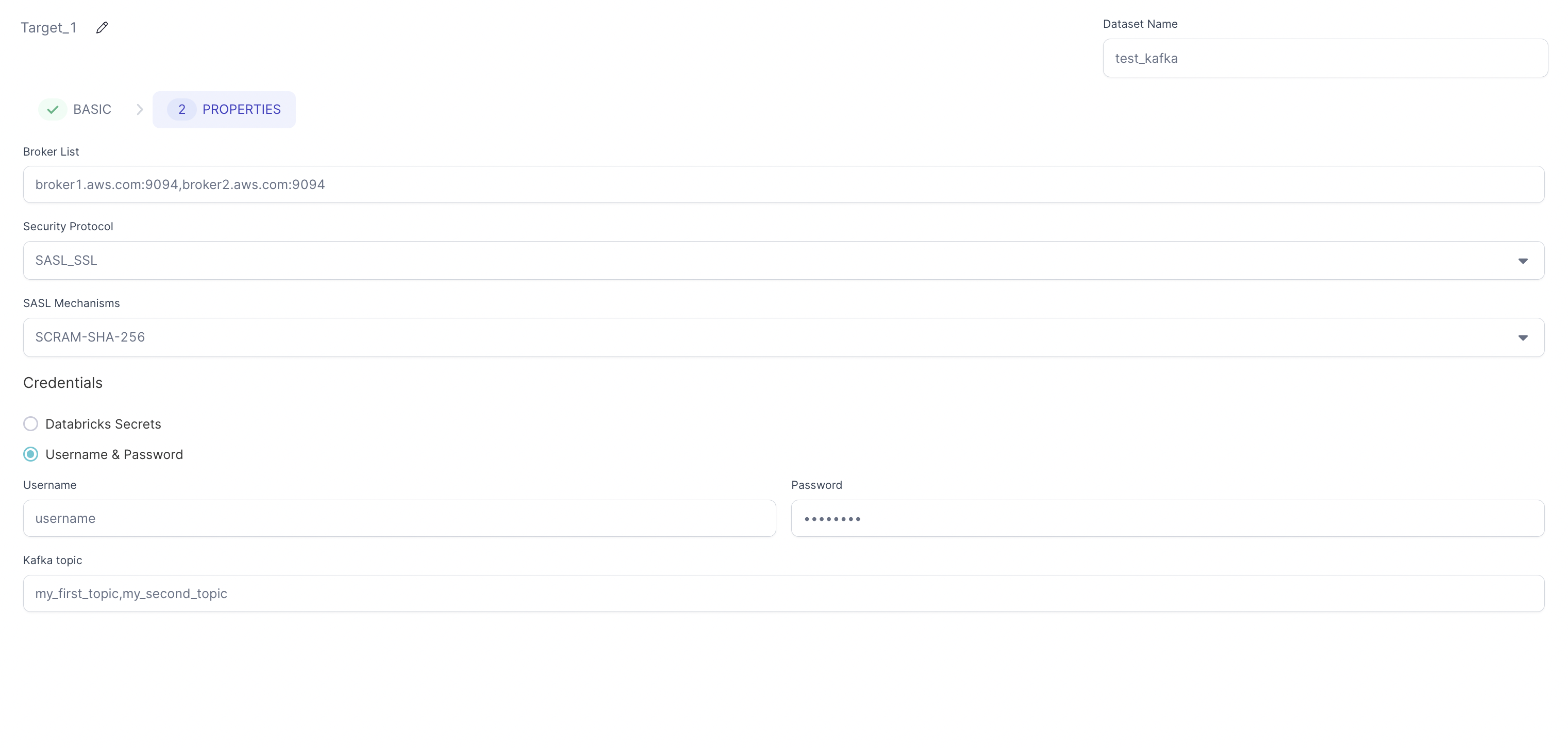
Target location
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Bootstrap Server/Broker List | Comma separated list of Kafka brokers. |
| Security Protocol | Security protocol for Kafka. Default value is NO_AUTH. |
| SASL Mechanisms | SASL Mechanism for authentication. Default value is NO_AUTH. |
| Credentials | How to provide your credentials. You can select: Databricks Secrets, Username & Password, Environment variables, or None |
| Kafka topic | Comma separated list of Kafka topics. |
| Message Unique Key (Optional) | Key to help determine which partition to write the data to. Used for message partitioning. |
| Use SSL Trust Store | Enable SSL trust store configuration. When enabled, requires Trust Store Location and Trust Store Password. |
| Trust Store Location | Path to the SSL trust store file. Required when SSL Trust Store is enabled. |
| Trust Store Password | Password for the SSL trust store file. Required when SSL Trust Store is enabled. |
Target properties
| Property name | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
| Kerberos service name for Kafka SASL | Name of your Kerberos service to use in Kafka. | None |
Example
Compiled code
To see the compiled code of your project, switch to the Code view in the project header.
- Python
def KafkaTarget(spark: SparkSession, in0: DataFrame):
df1 = in0.select(to_json(struct("*")).alias("value"))
df2 = df1.selectExpr("CAST(value AS STRING)")
df2.write\
.format("kafka")\
.options(
**{
"kafka.security.protocol": "NO_AUTH",
"kafka.sasl.mechanism": "NO_AUTH",
"kafka.bootstrap.servers": "broker1.aws.com:9094,broker2.aws.com:9094",
"topic": "my_first_topic,my_second_topic",
"kafka.ssl.truststore.location": "dbfs:/Volumes/tmp/kafka.client.truststore.jks",
"kafka.ssl.truststore.password": "password",
}
)\
.save()
Example Pipeline
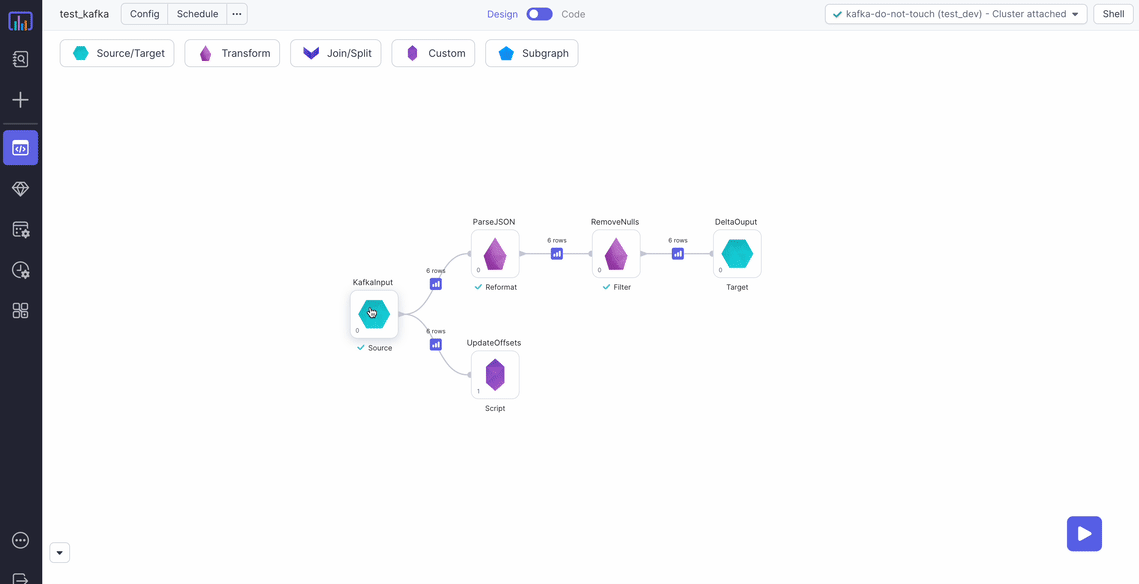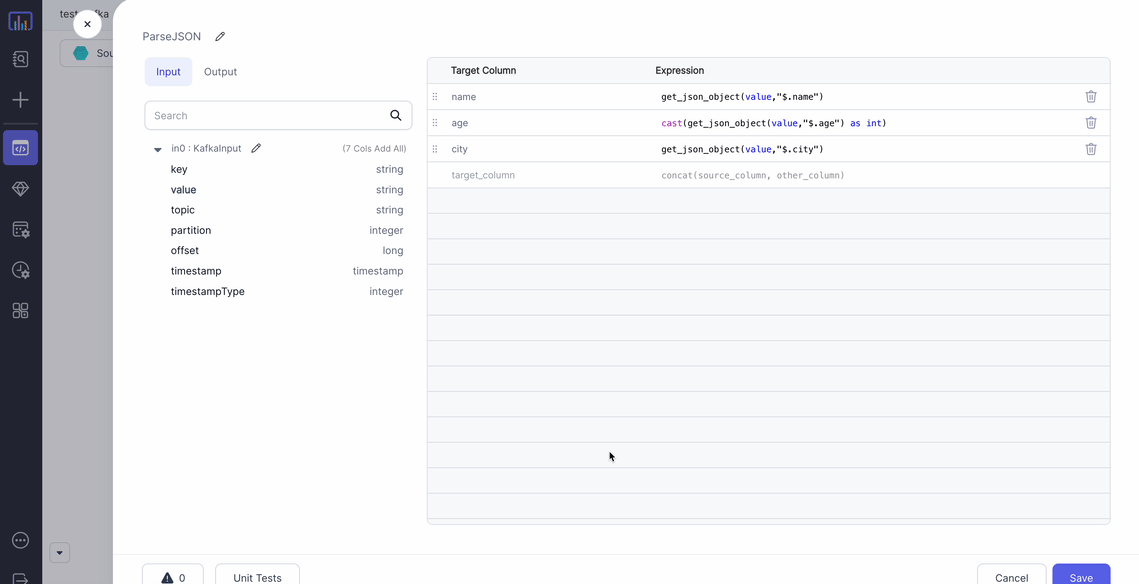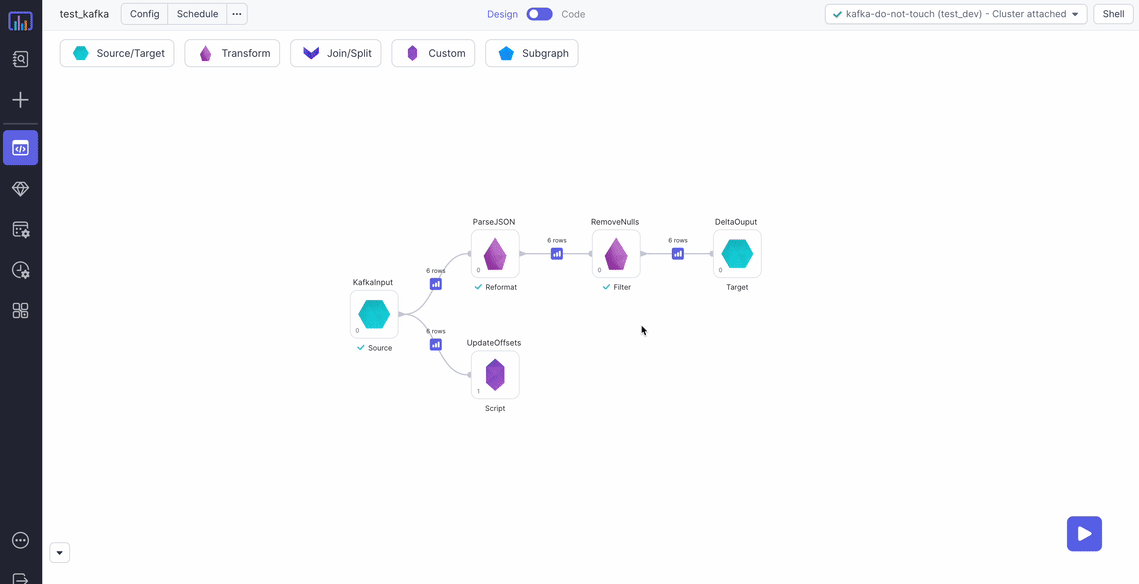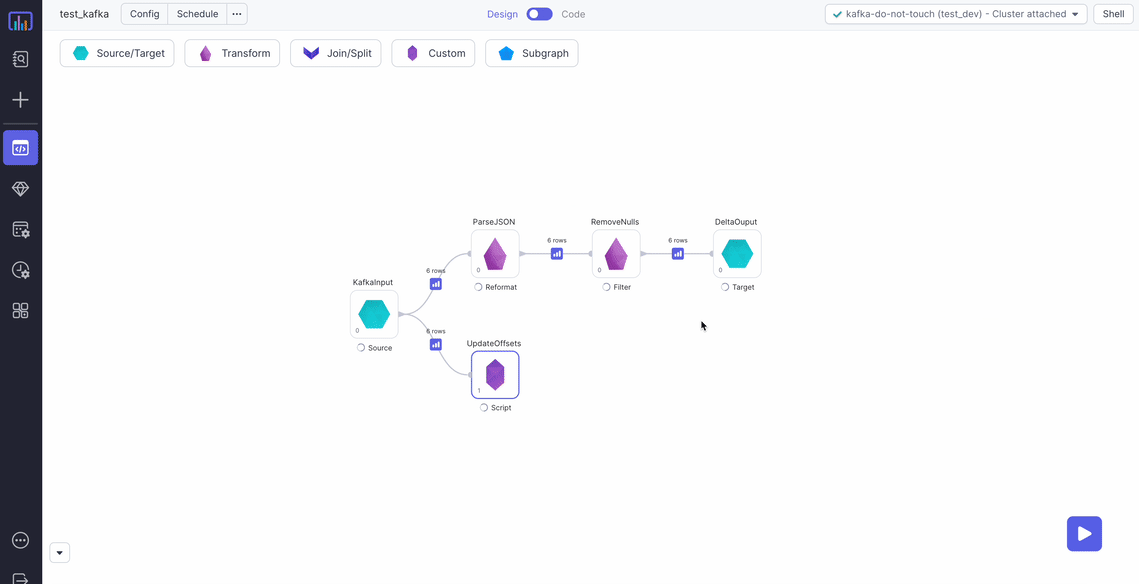
Source Pipeline Example
In this example, you read JSON messages from Kafka, parse them, remove any null messages, and persist the data to a Delta table.
To see the compiled code of your project, switch to the Code view in the project header.
Metadata Table
To avoid reprocessing messages on subsequent pipeline runs, update a table with the last processed offsets for each Kafka partition and topic. When you run the pipeline, the table only gets a batch of messages that arrived since the previously-processed offset.
In this example, you update metadata.kafka_offsets, which has the following structure:
| topic | partition | max_offset |
|---|---|---|
| my_first_topic | 0 | 10 |
| my_first_topic | 1 | 5 |
| my_second_topic | 0 | 10 |
| my_second_topic | 1 | 5 |
Taking this approach provides you the with following benefits:
- Builds the pipeline interactively without committing any offsets.
- Production workflows only consume messages that arrived since the previously-processed offset.
- You can replay old messages by modifying the Metadata table.
For production workflows the phase for the Script gem that updates the offsets should be greater than the phase of the Target gem. This ensures that offsets only update in the table after Prophecy safely persists the data to the Target.
Spark Code used for script component
To see the compiled code of your project, switch to the Code view in the project header.
- Python
def UpdateOffsets(spark: SparkSession, in0: DataFrame):
if not ("SColumnExpression" in locals()):
from delta.tables import DeltaTable
import pyspark.sql.functions as f
metadataTable = "metadata.kafka_offsets"
metaDataDf = in0.groupBy("partition", "topic").agg(f.max(f.col("`offset`").cast("int")).alias("max_offset"))
if not spark.catalog._jcatalog.tableExists(metadataTable):
metaDataDf.write.format("delta").mode("overwrite").saveAsTable(metadataTable)
else:
DeltaTable\
.forName(spark, metadataTable)\
.alias("target")\
.merge(
metaDataDf.alias("source"),
(
(col("source.`partition`") == col("target.`partition`"))
& (col("source.`topic`") == col("target.`topic`"))
)
)\
.whenMatchedUpdateAll()\
.whenNotMatchedInsertAll()\
.execute()